Regulating the brokering of small arms and light weapons

Especially since the 1990s, international transfers of SALW and ammunition have been conducted in increasingly differentiated markets. A multitude of products, buyers and suppliers around the world, including State-owned entities and large defence manufacturers, use the services of specialist intermediaries, as well as private agents and dealers. States often use brokering services for the purpose […]
International standards to prevent police gun violence

In many countries, the global and regional proliferation of small arms means that police and other law enforcers are under extreme pressure to counter rising levels of violent gun crime, and are expected to confront armed offenders. In the process, ill-trained and ill-disciplined officers with guns, sometimes kill, maim, and mistreat innocent people whom they are supposed to protect. Increasingly, police, customs and other law enforcement officers are also called upon to detect illicit gun traffickers, mark firearms, process firearms licenses, collect illicit firearms and persuade communities to report illegal firearms. However, such efforts are often thwarted by corrupt police practices and a lack of trust from communities.
IANSA has published a briefing paper and Fact Sheet on “International Standards to Prevent Police Gun Violence.” This publication focuses on essential common principles and procedures which the United Nations has recommended to ensure that all law enforcement agencies will restrict their use of force to a minimum, keep their firearms under strict control, and prevent officers from committing acts of gun violence or other abuse. The UN standards draw on international human rights law, general principles on the rule of law, and provide guidance to differentiate between a lawful use of force and firearms, as opposed to acts of criminal violence by the police.
Post-shipment control of small arms and light weapons

The illicit trade of small arms and light weapons (SALW) and their ammunition, parts and components remains a serious international problem in many States. To prevent the illicit trade in conventional weapons and to prevent their diversion to the illicit market, all States have made commitments since 2001 to establish stronger systems that will ensure […]
Children shooting children

This paper aims to explain how small arms and light weapons (SALW) proliferation leads to extreme violence by children using guns against other children, a shocking indictment on the failure of governments to ensure strict control of such weapons. The paper will draw on examples from different countries where such incidents have occurred. It will […]
Small arms and light weapons proliferation and violence: Estimating its scale and forms
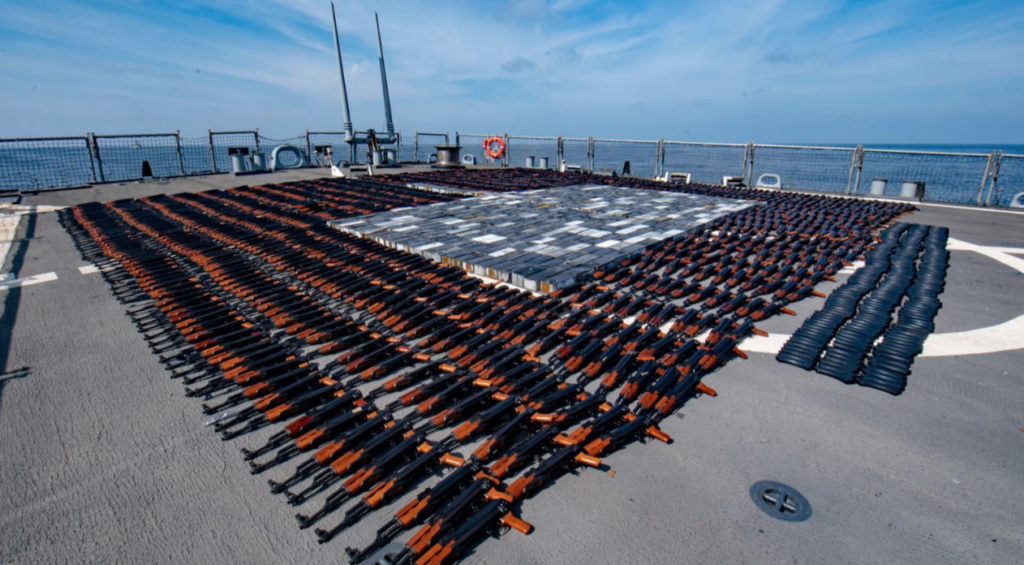

aSmall arms and light weapons are widely available and easy to use, so they are the most prominent tools in contemporary armed conflicts as well as in armed criminal and interpersonal violence in non-conflict settings. To grasp the global scale of SALW proliferation and the patterns of violence committed with SALW, this briefing paper summarizes […]
Africa and the ‘grey market’

Arms brokering or inter-mediation is a commercial activity within the international arms trade that is difficult to regulate. Arms brokers often operate transnationally, so often escaping or avoiding national trade controls in their home countries and the countries where transactions have taken place. Their transnational operations also create “grey” markets, which sometimes fuel illicit markets. […]
Opinion on the Legality of Arms Transfers to Saudi Arabia, The United Arab Emirates and other members of the coalition militarily involved in Yemen

This opinion addresses the legality under international law of the transfer of conventional arms and related equipment to the parties currently engaged in the conflict in Yemen. The opinion does not assess the legality of the export, import or sale of arms to those parties in the light of the domestic law of each supplying […]
Article – The Political Economy of Roadblocks in the Central African Republic
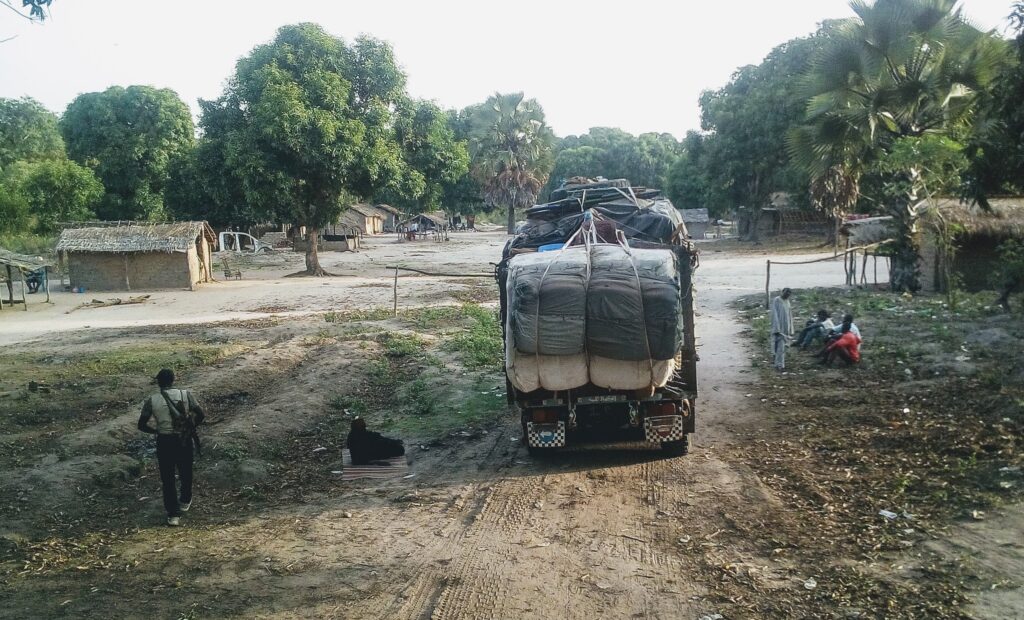

From September 2016 to September 2017, the International Peace Information Service (IPIS) and the Danish Institute for International Studies (DIIS) conducted a mapping of roadblocks in the Central African Republic. This data collection campaign also features more than 200 interviews with various actors and was combined with data from other reports on roadblocks to form […]
Towards a multi-scale approach for an Earth observation based assessment of natural resource exploitation in conflict regions
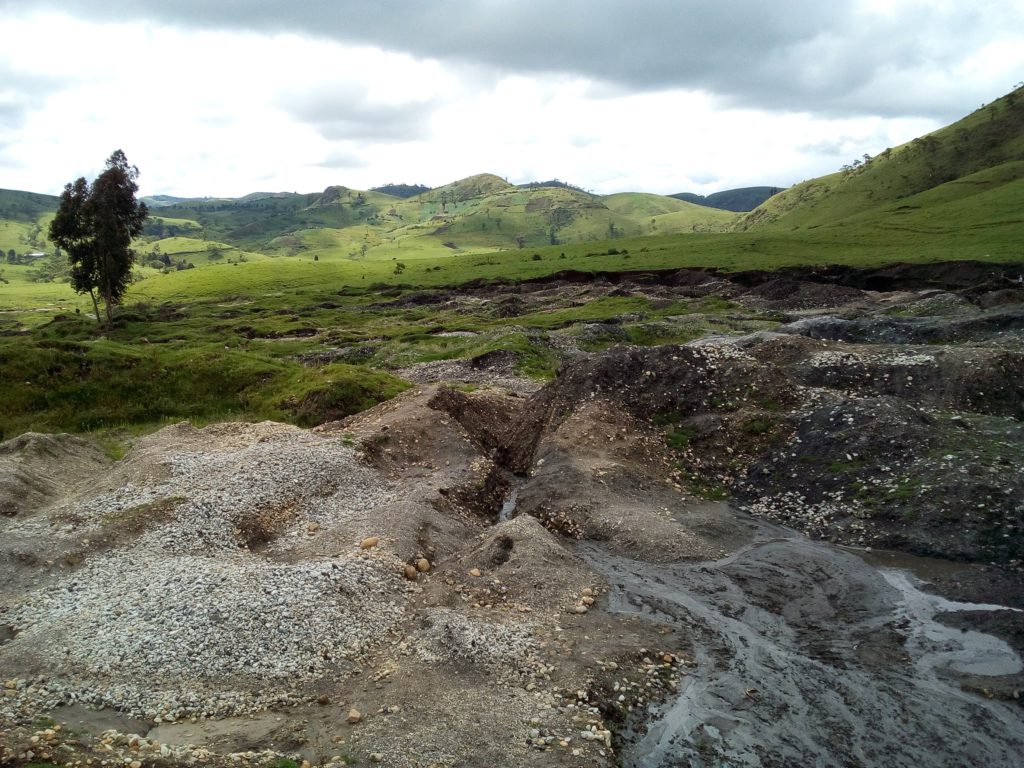

Environment and natural resources can be key elements in starting and fueling conflicts. IPIS researcher Filip Hilgert contributed to an article in Geocarto International (2017, vol. 32, n° 10) on a multi-scale approach for an Earth observation based assessment of natural resource exploitation in conflict regions. Download the full article Elisabeth Schoepfer, Kristin Spröhnle, Olaf […]
Optimalisatie van het wapenhandeldecreet en wapenhandelbesluit: advies van IPIS en Amnesty International Vlaanderen

In maart 2012 publiceerden Amnesty International Vlaanderen en IPIS een nota met analyse en aanbevelingen bij het ontwerp van decreet “betreffende de in-, uit-, doorvoer en overbrenging van defensiegerelateerde producten, ander voor militair gebruik dienstig materiaal, ordehandhavingsmateriaal, civiele vuurwapens, onderdelen en munitie”. Het uiteindelijke ‘Wapenhandeldecreet’ van 30 juni 2012 schiep een geheel nieuw regelgevend kader, […]
Accessible and Interactive: New Methods of Data Visualization as Tools for Data Analysis and Information Sharing in Transitional Justice Research
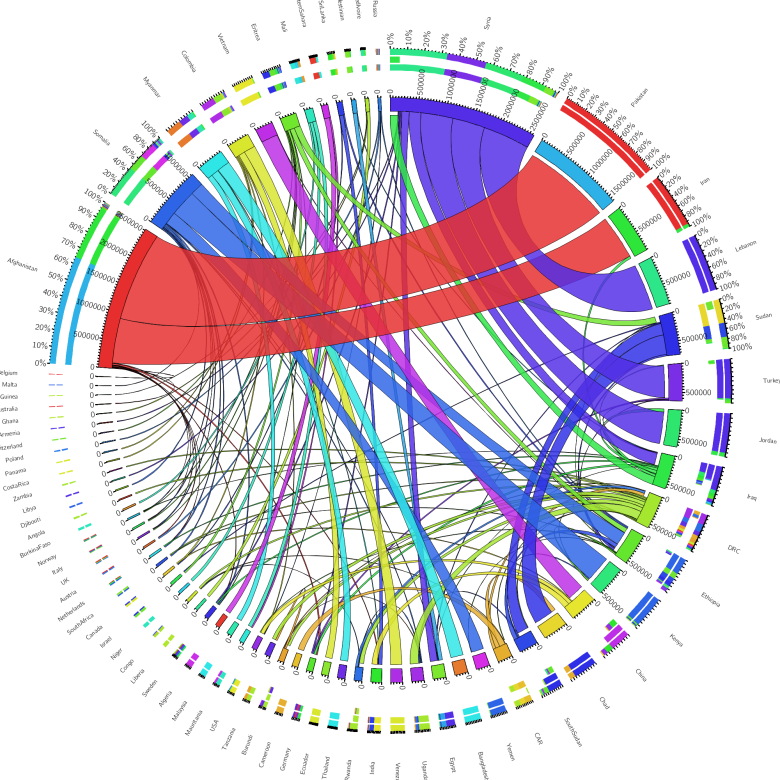
Abstract The production and use of datasets is a growing area in transitional justice research. One constant limitation, however, is the way this data is visualized. Relying only on static graphics and tables, many of these datasets are insufficiently explored and analyzed, and remain inaccessible for other researchers. Interactive data visualization tools are an ideal […]
Weapons and International Law: the Arms Trade Treaty

IPIS is pleased to announce its contribution to a new book on the Arms Trade Treaty published by Larcier. Weapons and International law: The Arms Trade Treaty gives a thorough legal and practical analysis of this important new legal instrument to regulate the global trade of the most commonly-used conventional arms. Amongst our IPIS personnel, Brian […]
Informal Expert Group Meeting, United Nations Institute for Disarmament Research (UNIDIR), Vienna, 22–23 April 2015

Between 22–23 April 2015 IPIS was invited to participate in a two-day informal expert group meeting for UNIDIR’s project “Examining Options and Models for Harmonization of End Use/r Control Systems” (http://www.unidir.org/programmes/process-and-practice/examining-models-for-harmonization-of-end-use-r-control-systems). The objective of the informal expert meeting was to review common positions on practices and procedures, as well as to explore approaches and methods […]
Carburante Usa ai jet israeliani

Download in pdf or open with issuu reader.
Wereldbeeld: Nieuwste VN-vredesmissie start in de Centraal- Afrikaanse Republiek: Geweld, een zwakke veiligheidssector en de rol van de internationale gemeenschap. Lotte Hoex. pp 6-13

Om burgers te beschermen tegen het aanhoudende geweld in de Centraal-Afrikaanse Republiek (CAR), ging op 15 september 2014 de nieuwste vredesmissie van de Verenigde Naties (VN) van start. De CAR ligt in centraal Afrika, telt vijf miljoen inwoners en is één van de armste landen ter wereld. Sinds de onafhankelijkheid van Frankrijk in 1960 kampt […]
Boundary spanning: moving towards strategic stakeholder engagement

In today’s globally expanded production and supply chains, most companies have a hard time living up to their commitment to operationalize business & human rights principles. Countless multinational companies, State-owned enterprises (SOEs) and small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in different countries, and across all industry sectors, have faced allegations of labor rights violations, human rights […]
Strijd tegen conflictmineralen: sleutel tot conflictresolutie in Oost-Congo?
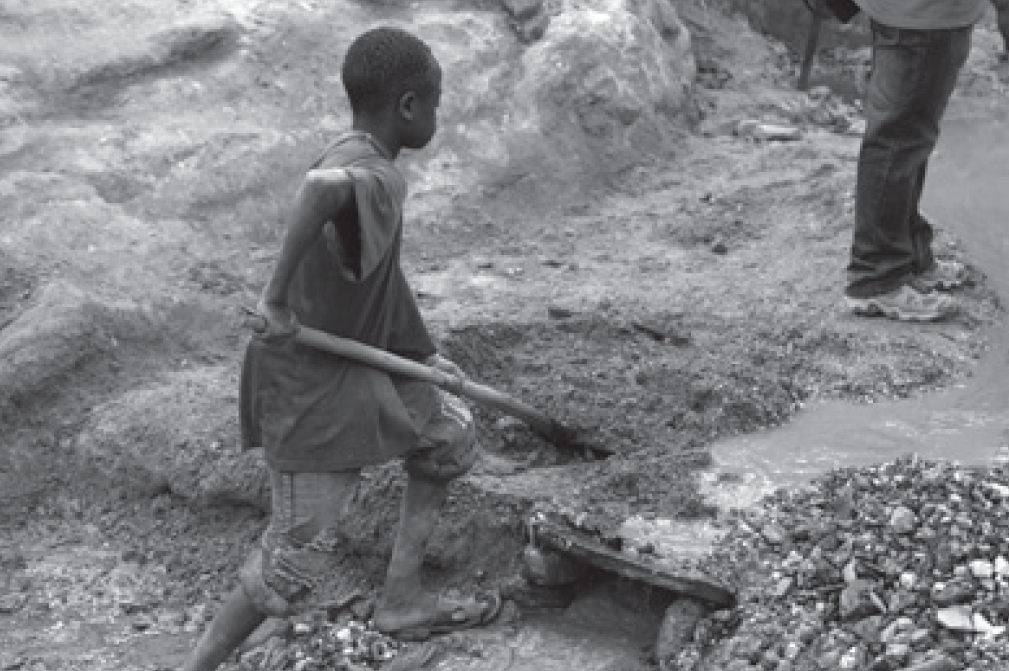

De PDF van dit artikel is met toestemming van de redactie overgenomen uit de /Internationale Spectator, Clingendael Magazine voor Internationale Betrekkingen/, uitgegeven door de Koninklijke Van Gorcum, te Assen namens het Nederlands Instituut voor Internationale Betrekkingen ‘Clingendael’ te Den Haag. Download in pdf of open met issuu reader.
Major Powers Fuelling Atrocities. Why the world needs a robust Arms Trade Treaty
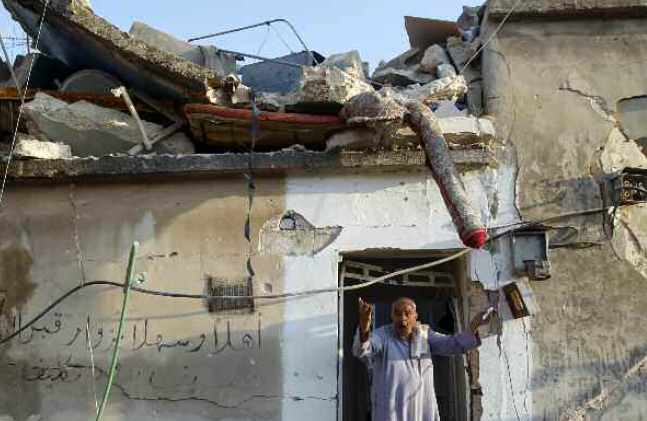

IPIS contributed to the research for this AI report. Every year, thousands of people are killed, injured, raped and forced to flee from their homes as a result of abuses and atrocities committed with conventional arms and ammunition. Harrowing testimonies and images from conflict zones and human rights crises around the world underline the urgent […]
The Arms Trade Treaty: Building a Path to Disarmament

The goal of this article is to examine and suggest proposals that could enhance the role of the international Arms Trade Treaty—presently in discussion at the United Nations—in the regulation of the international arms trade and in addressing the role of the legal trade in: a) providing the bulk of the arms used in armed […]
Upstream Implementation of the OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals from Conflict-Affected and High-Risk Areas. Final Report on one-year pilot implementation of the Supplement on Tin, Tantalum, and Tungsten

Final Report on one-year pilot implementation of the Supplement on Tin, Tantalum, and Tungsten. This report is the final in a cycle of three reports on the pilot implementation by upstream companies of the “Supplement on Tin, Tantalum and Tungsten of the OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals from Conflict-Affected and […]

